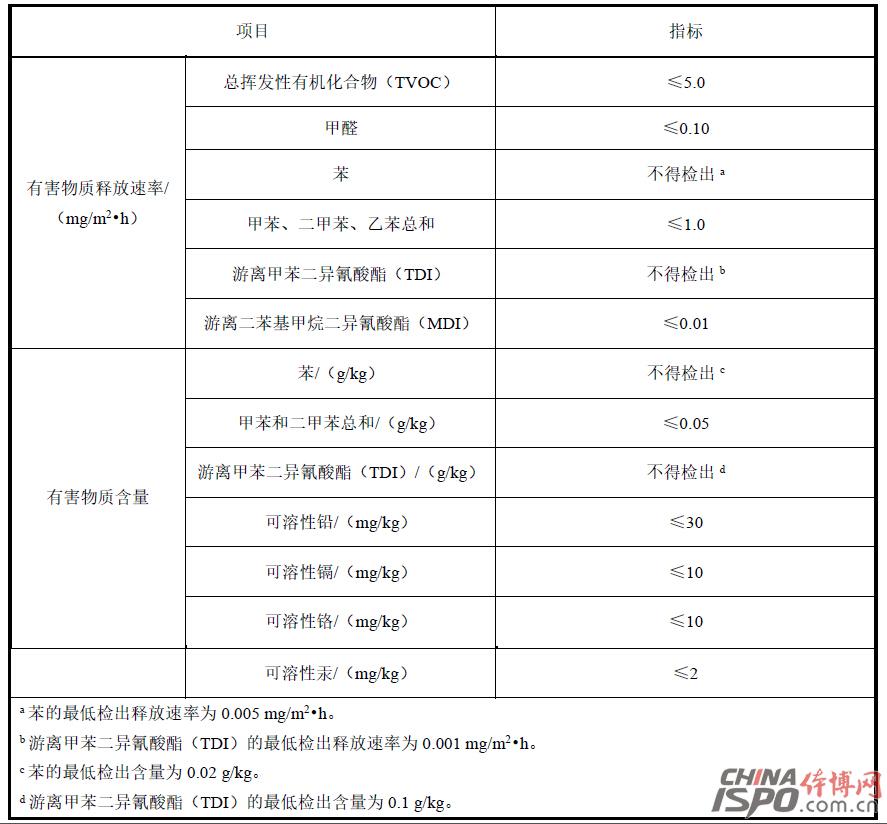
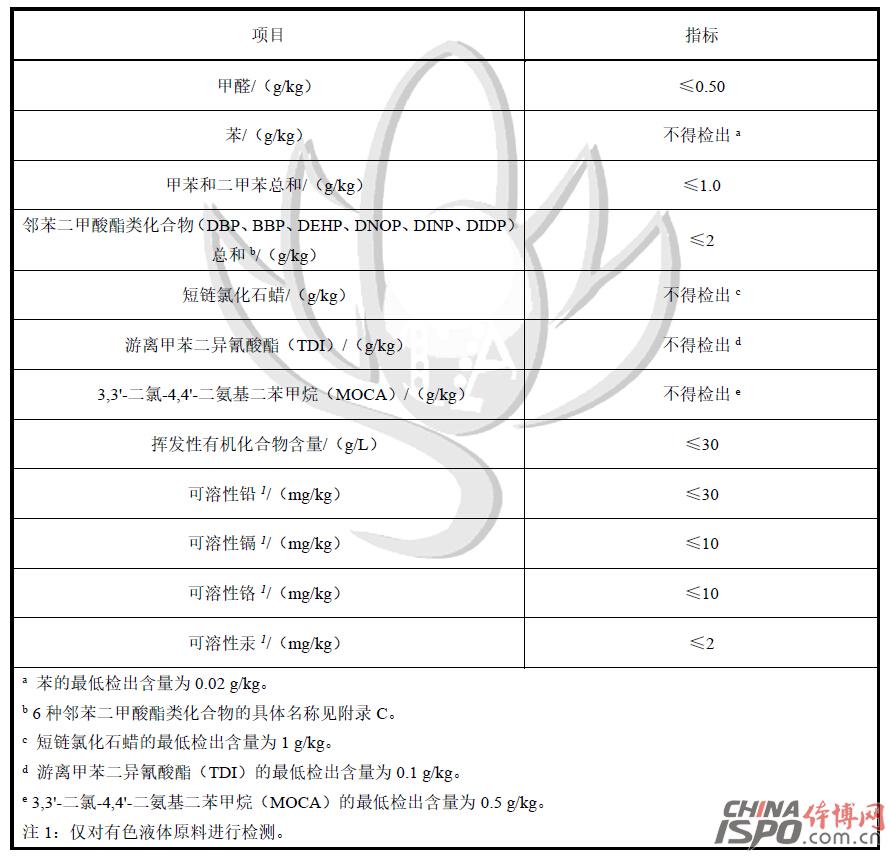
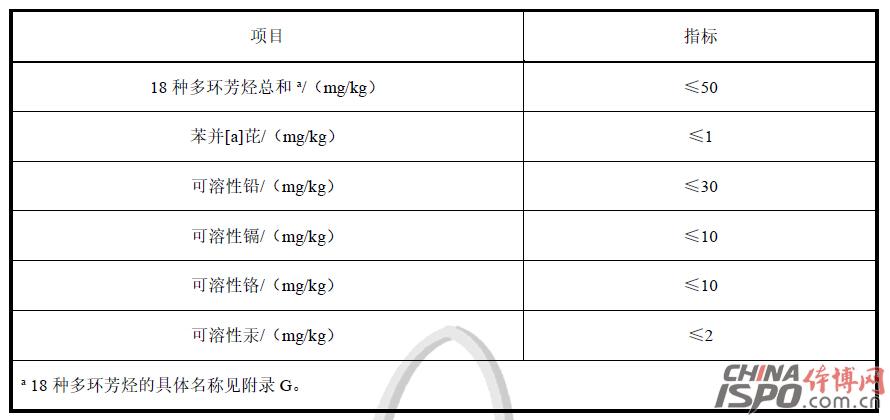
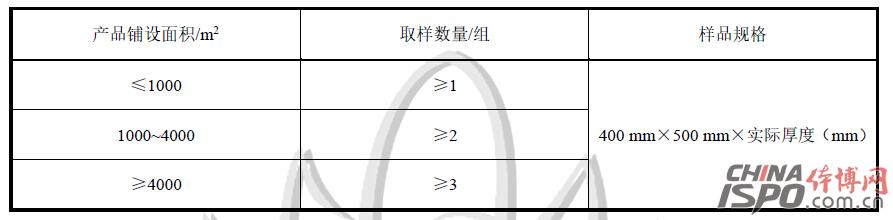
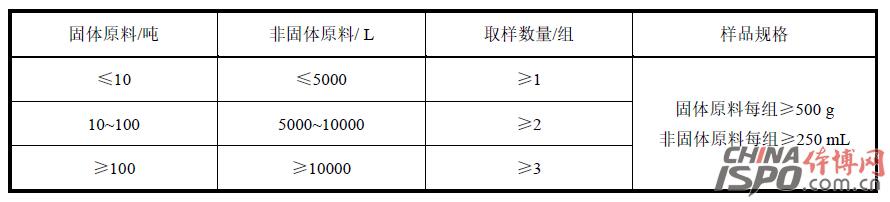
Foreword This standard was drafted in accordance with the rules given in GB/T 1.1-2009. This standard was proposed by the Shanghai Chemical Building Materials Industry Association and the Shanghai Consumer Rights Protection Committee. This standard entrusts the Shanghai Chemical Building Materials Industry Association to be responsible for interpretation. The main drafters of this standard: Shanghai Chemical Building Materials Industry Association, Shanghai Jianke Inspection Co., Ltd., Shanghai Chemical Building Materials Industry Association Flooring Materials Branch, Shanghai Chemical Building Materials Industry Association Waterproof Materials and Construction Technology Branch, East China University of Science and Technology, BASF Polyurethane Specialty Products (China) Co., Ltd., Dow Chemical (China) Investment Co., Ltd., and Shanghai Taian Industrial Group Co., Ltd. Participated in the drafting of this standard: Shanghai Jiansheng Sports Field Engineering Co., Ltd., Jiangmen Changhe Chemical Industry Group Co., Ltd., Shanghai Huiyu Fine Chemicals Co., Ltd., Jiaxing Green Energy Plastic Products Co., Ltd., Shanghai Hangkuang Stadium Facilities Engineering Co., Ltd., and Shanghai Olympics Project Co., Ltd., Shanghai Tuocheng Environmental Protection Engineering Co., Ltd., Fujian Aoxiang Sports Plastics Technology Co., Ltd., Shanghai Dexin Construction Engineering Co., Ltd. Drafters of this standard: Lou Minggang, Yang Yong, Che Yanping, Lu Jingzhou, Fu Hui, Qi Chunyuan, Zhao Jianfei, He Jiaxu, Gu Jiayi, Tang Wei, Lin Biao, Zhuang Jiren, Liu Shuai, Zhang Liang, Zhu Limei, Zhao Wenhai, Wang Weiqin Lu Jun, Yu Xun, Gu Aibin, Lin Fanqiu, Wang Jian, Hu Yu, Zhang Chujie. This standard was first released in April 2016. School sports venues plastic surface layer harmful substances limit 1 Scope This standard stipulates the terms and definitions, requirements, test methods, inspection rules, and test reports for the limits of hazardous substances in plastic surfaces of school sports venues. This standard applies to all types of schools outdoor sports venues with plastic surface and raw materials. Plastic surfaces and raw materials used in other places can also be referred to. 2 Normative references The following documents are indispensable for the application of this document. For dated references, only the chronological version applies to this document. For those cited documents that do not note the time, the latest version (including all amendments) applies to this document. GB 18583-2008 Limits of harmful substances in adhesives for interior decoration materials GB/T 6682-2008 Analytical laboratory water specifications and test methods GB/T 6750-2007 Determination of density of paints and varnishes Pycnometer method GB/T 10111-2008 Generation of Random Numbers and Its Application in Product Quality Sampling Inspection GB/T 14833-2011 synthetic track surface layer GB/T18204.2-2014 Sanitary inspection methods for public places Part 2: Chemical pollutants GBZ/T160.67-2004 Workplace atmosphere toxic substances Determination of isocyanates ISO 16000-3 Indoor air - Part 3: Determination of formaldehyde and other carbonyl compounds in indoor air and laboratory atmospheres - Active sampling method (Indoor air - Part 3: Determination of formaldehyde and other carbonyl compounds in indoor air and test chamber air - Active Sampling method ISO 16000-6 Indoor Air Part 6: Determination of Indoor and Laboratory Air by Tenax TA Adsorbent, Thermal Desorption, and Gas Chromatography Active Sampling Using Mass Spectrometry (MS) or Mass Spectrometry-Flame Ionization Detectors (MS-FID) Volatile Organic Compounds (Indoor air - Part 6: Determination of volatile organic compounds in indoor and test chamber air by active sampling on Tenax TA sorbent, thermal desorption and gas chromatography using MS or MS-FID) 3 Terms and Definitions The following terms and definitions apply to this standard. 3.1 Plastic surface plastic and rubber sports surface Refers to the use of binders, polymer particles, supplemented by synthetic materials such as pigments, additives, fillers, etc., through a certain construction process or prefabricated surface materials, not including non-synthetic material parts of the laying site (eg soil-based, concrete Layers, etc.) 3.2 Plastic surface solid raw materials for plastic and rubber sports surface Refers to synthetic materials that exist in solid form during construction, such as black rubber particles, EPDM rubber particles, or PU particles and other high-molecular particles. 3.3 Non-solid raw materials for plastic and rubber sports surface Refers to synthetic materials that exist in non-solid form during construction, such as adhesives, surface sprays, and the like. 3.4 Volatile Organic Compounds volatile organic compounds (VOC) At the standard pressure of 101.3 kPa, any organic compound with an initial boiling point of less than or equal to 250 °C. 3.5 Total Volatile Organic Compounds total volatile organic compounds (TVOC) Samples were analyzed on a non-polar column (polarity index less than 10) using Tenax TA sampling and the retention time was the sum of volatile organic compounds between n-hexane and n-hexadecane. 4 Requirements 4.1 Requirements for Limits of Harmful Substances in Finished Plastic Products The limit of harmful substances in the finished product of plastic surface shall comply with the requirements in Table 1. Table 1 Limits of harmful substances in finished plastic products 4.2 Limits of harmful substances in plastic surface materials 4.2.1 The limits of harmful substances in non-solid materials shall meet the requirements in Table 2. Table 2 Specifications of hazardous substances in non-solid raw materials 4.2.2 The limits of hazardous substances in solid raw materials should meet the requirements in Table 3. Table 3 Limits of harmful substances in solid materials 5 test methods 5.1 Sample Preservation Environmental Conditions Use a storage environment with a temperature of (23 ± 2) °C and a relative humidity of (50 ± 10)% RH. 5.2 Limits of harmful substances in finished plastic products 5.2.1 Determination of the rate of release of harmful substances from plastic surface finishes is carried out in accordance with the method specified in Appendix A of this standard. 5.2.2 Determination of the sum of benzene, toluene and xylene in the finished product of the plastic surface layer and determination of free toluene diisocyanate (TDI) According to the method specified in GB/T 14833-2011, the sample preparation is in accordance with Appendix B B.5.1 of this standard The method specified in .1 is performed. 5.2.3 The determination of soluble lead, cadmium, chromium, and mercury in the finished plastic surface shall be carried out in accordance with the method specified in Appendix B of this standard. 5.3 Limits of harmful substances in plastic surface materials 5.3.1 Harmful Substances in Non-solid Raw Materials 5.3.1.1 The determination of the sum of formaldehyde, benzene, toluene, and xylene in the non-solid raw materials and the determination of free toluene diisocyanate (TDI) is carried out according to the method specified in GB 18583-2008. 5.3.1.2 Determination of phthalate ester compounds in non-solid raw materials is performed in accordance with the method specified in Appendix C of this standard. 5.3.1.3 Determination of short-chained chlorinated paraffins in non-solid materials is performed in accordance with the method specified in Appendix H of this standard. 5.3.1.4 The determination of 3,3'-dichloro-4,4'-diaminodiphenylmethane (MOCA) in non-solid raw materials is carried out in accordance with the method specified in Appendix D of this standard. 5.3.1.5 Determination of Volatile Organic Compounds in Non-Solid Raw Materials Follow the method specified in Appendix E of this standard. 5.3.1.6 Determination of soluble lead, cadmium, chromium, and mercury in non-solid raw materials is performed according to the method specified in Appendix B of this standard. 5.3.2 Limits of Harmful Substances in Solid Materials 5.3.2.1 The sum of the 18 PAHs in the solid material and the determination of benzo[a]pyrene are performed in accordance with the method specified in Appendix G of this standard. 5.3.2.2 The determination of soluble lead, cadmium, chromium, and mercury in solid materials is performed in accordance with the method specified in Appendix B of this standard. 6 Inspection Rules 6.1 Witness sampling Samples of plastic surface materials used in all construction processes and plastic surface products after completion shall be conducted under the witness of a third party. 6.2 Sampling requirements 6.2.1 The same kind of plastic surface layer in each project is a batch. The sampling amount for each batch is as specified in Table 4: Table 4 Samples of plastic surface layers 6.2.2 After the construction of the plastic floor, the curing time shall be at least 14 days under field conditions after construction. If the sample is not completely cured within 14 days, the curing time at the construction site may be appropriately prolonged, but no accelerated curing such as heating may be used. The time must not exceed 28 days. 6.2.3 Samples should be taken directly from the plastic field after completion of construction. Refer to Appendix I for rules for determining the location of samples for excavation. After digging the samples, seal them with polyethylene or PTFE bags and store them in a cool, dry place. After the sample is selected, it should be delivered to the laboratory within 48 hours and the test should begin as soon as possible. 6.2.4 At least one sample shall be taken for each type of raw material of plastic surface layer, and the specific sample volume of each type of raw material is shown in Table 5. Table 5 Samples of plastic surface raw materials 6.2.5 Raw materials for plastic surface should be sampled before entering the site. Non-solid raw materials should be fully stirred into a clean glass or PTFE bottle sealed and preserved; solid raw materials sampled into a polyethylene or PTFE bag sealed and stored. 6.3 Decision Rules When the test results of all items in each group of samples meet the technical requirements of this standard, it is determined that the samples in the group meet the requirements of this standard; if any one of the samples does not meet the technical requirements of this standard, it is determined that the group of samples does not meet the requirements of this standard. 7 Test report The test report should contain at least the following information. a) The date the sample was delivered to the laboratory; b) sample test results and determination; c) description of the sample state, such as color, thickness, etc.; d) Provide multiple sets of distribution ratio information as necessary; e) Project name, sampling date, curing time, sampling site, etc.; f) Photo of the sample. Note: Due to length, full content, please download the document to continue reading Baby High Chair,Baby Safety Chair,High Chair For Baby,Baby Table Chair Zhejiang Lamon Technology Inc. , https://www.baby-chaires.com