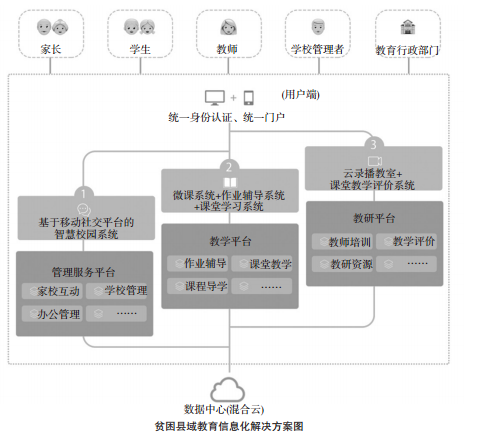
First, the question is raised The development of education in rural poverty-stricken areas has always been the focus and difficulty of social attention. In recent years, people have become more aware that educational informationization may be an effective way to solve this problem [1][2]. In a congratulatory letter to the first International Education Informatization Conference, the Chairman pointed out that it is necessary to "gradually narrow the regional and urban-rural digital gap through education informatization and vigorously promote education equity"; the Deputy Prime Minister in the second national video conference on education informationization It is proposed to "strengthen the effectiveness of informatization in promoting education equity, improving education quality, and promoting the transformation of teaching methods, management models, and educational service supply methods" [3]; "Education Informatization" 13th Five-Year Plan It also clearly puts forward the important goal of “prioritizing the promotion of education informatization to promote educational equity and improve the quality of educationâ€. It is not difficult to see that education informatization has been highly anticipated in promoting education equity and promoting education development in rural poverty-stricken areas. The promotion of informatization is a capital-intensive and intellectually intensive work. It is difficult and important to promote education informatization in rural poverty-stricken areas where funds, resources and manpower are scarce. It can be said that education informatization in rural poverty-stricken areas is The tough battle in the overall strategy of education informationization in China. During the "Twelfth Five-Year Plan" period, with the great attention of governments at all levels, important progress has been made in education informatization in rural poverty-stricken areas in the central and western regions; how to continue to exert efforts during the 13th Five-Year Plan period to further break through the bottleneck and promote rural poverty-stricken areas The level of education informatization makes education informatization truly play a role in comprehensively promoting education modernization in rural poverty-stricken areas. It is a problem that both the government and the academic circles need to face squarely [4]. This paper attempts to clarify the characteristics of education development in rural poverty-stricken areas from the current situation of education development in rural poverty-stricken areas, and on this basis, to explore the development model of education informatization in rural poverty-stricken areas with practical and scalable. Second, the "13th Five-Year Plan" in rural poverty-stricken areas The advancement of informatization has its significant phase characteristics. Before discussing the promotion mode of education informatization in a region and a period of time, we must first clarify the phase characteristics of the educational informatization process in this region and during this period. It should be pointed out that China has a vast territory and different economic and social backgrounds and development trends. The so-called rural poverty-stricken areas cannot accurately reflect the actual situation of specific areas. The causes of poverty vary from place to place, and the situation of poverty alleviation varies greatly. Interesting), therefore, we can only describe the staged characteristics of educational informationization in rural poverty-stricken areas from a macro perspective [5]. First, the level of education information infrastructure construction in rural poverty areas has been greatly improved. During the “Twelfth Five-Year Plan†period, the Internet access rate of primary and secondary schools nationwide has reached 87%, and the penetration rate of multimedia classrooms has reached 80% [6]. According to the unified deployment of the Ministry of Education, the Internet access rate of primary and secondary schools in China should reach 95% in 2016, of which the proportion of broadband access above 10M should reach more than 60%; the proportion of urban and rural primary and secondary schools equipped with multimedia teaching equipment in ordinary classrooms of schools respectively To achieve 80% and 50%, the basic realization of the national primary and secondary schools have multimedia teaching conditions [7]. The teaching points have also achieved full coverage of digital education resources. It can be expected that by 2020, all schools and teaching points in rural poverty-stricken areas in the country will basically have access to networks and equipment. It is obvious that infrastructure and hardware equipment are not the core issues that restrict the development of educational information in rural poverty areas. Second, lack of systems, less applications, and fewer resources are the current rural poverty. The general phenomenon in the development of regional education informationization. “Reconstruction and light use†has always been a common problem in the process of promoting the development of education informatization in various parts of China. This problem is particularly common in rural poverty-stricken areas. If the main reason for the problem of “reconstruction and light use†in developed areas is “use and not use†caused by unfriendly users of software systems, then rural poverty-stricken areas are truly “nothing availableâ€. The direct result of this is that the country has spent a lot of energy and the infrastructure of large capital construction is ineffective (at least not able to fully exert its construction benefits), and on the other hand, many people have begun to question the necessity of continuing to promote education informationization. Third, the lack of personnel, funds and resources is still the constraint for the development of education and the informatization of education in rural poverty areas in the future. Take S County, a national poverty-stricken county in J Province as an example. There are 374 public schools in the county, including 104 teaching points. The number of primary and middle school students is 124,500, but the funds for education projects in the past five years are only 119 million yuan (even if not counted). The teaching points, regardless of public funds, the average annual educational project funds per school is less than 90,000 yuan, and the investment in education information funds is only 61.5 million yuan (each school's annual education informationization funds are less than 50,000 yuan). Even with a growth rate of 10% per year, the funding will not change much by 2020. In addition, there are only 114 people in the county's educational informationization staff (full-time 48 people, 64 part-time jobs. Among them, 2 are audio-visual stations, only one person is born in the class). It can be said that during the 13th Five-Year Plan period, the main task of promoting education informatization in rural poverty-stricken areas is to realize educational informationization based on the educational information facilities and facilities that have begun to take shape in the context of relatively scarce personnel, funds and resources. Effective application. 3. The model for promoting education informatization in developed regions cannot be copied to rural poverty-stricken areas. The so-called educational informatization promotion model mainly refers to three issues to be considered in the process of promoting education informatization: First, who will lead, that is, who will pay the funds and who will manage it; second, the importance of education, education information It is a large category. In general, it includes teaching informationization, management informationization, and service informationization. The so-called scornfulness refers to the integration of the process in the process of promotion, or focus on it; After you first squat, you can build it first, and then build it later. The so-called "promoting mode of education informatization in rural poverty-stricken areas" is to answer these three questions. For a long time, there has been a concept in the field of education and education informatization, that is, advanced areas in the developed areas, advanced learning experiences in developed areas in rural poverty areas, and follow-up strategies. So what is the so-called "advanced experience" in developed regions? Here we will use the S city M district and its G school as an example to explore. G School is an ordinary public high school in the M District of S City. Its average score of the college entrance examination (excellent class) is long in the M area. In 2013, the school began to cooperate with an educational information enterprise to promote “smart education†(the so-called cooperation promotion refers to the idea of ​​M school, a small part of the funds, the majority of the company's funds, technical strength), and established The pre-class "micro-course guidance", the "smart classroom" in the class, and the "homework guidance" after class are the information-based teaching mode. In just over two years, the school has gone through various aspects such as planning, platform architecture, model certification, teaching experiment, hardware construction, and all-staff training. A series of teaching experiments have been carried out from point to point. And formed a certain scale, the teaching mode carried on the e-book bag has been able to be put into normal application, which promotes the overall improvement of teaching quality. The M District School of Education, where G School is located, has established a demand-oriented teacher professional development support system by working with a certain operator to focus on the professional development of teachers. The so-called cooperation refers to the idea of ​​the education institute and the technology of the operator. Strength, the construction education college of the system did not invest in the previous period, but offset the money by the bandwidth provided by the M district government to purchase the supplier to support the operation of the teacher development support system. The system integrates the M-zone teacher training network, the cloud recording and broadcasting classroom evaluation system, the academic quality analysis system, the teacher professional development system, etc., and has innovated the teaching and research research and teacher training methods through information technology, and built a training community, a special team and teachers. The individual learning space provides support and services for the education and teaching reform and professional development of teachers in the region. The above G school and M district education colleges represent the typical educational informationization promotion path in developed regions, focusing on teaching and teaching. We can see the general characteristics of this model: First, school-enterprise cooperation. In these two cases, the school (school) is the provider of ideas. The reason why enterprises are willing to give this school and the first house is because they can obtain rare educational experience from this school and the first hospital. It is not difficult to see that this model puts forward a high human resource requirement for the school and the school. In fact, the “top leaders†of the G school and the M district education college are both “shoulders and talents†who understand both teaching and information. . The second is to achieve a win-win situation. Obviously, both parties have achieved benefits in the cooperation. As for the school and the college, the expenses have been reduced. As far as the enterprise is concerned, both the experience and the experimental site have been obtained, and the enterprise has been able to upgrade its management level (in fact, with the M school). After the cooperation, the company's teaching information system has been further improved and achieved high economic benefits. From the example of the M District Education College, although the company has invested a system development income in the short term, it is considered. Bandwidth sales revenue has a certain profit margin in the long run. The third is the promotion of this level. In the above two cases, the initiators and promoters of informationization are the institutes and the schools themselves. The two “top leaders†of the G school and the M district education college start from the profound understanding of information technology support education and teaching, and show in the process of informationization. Strong resource integration and problem solving skills are especially valuable. From these three characteristics, we can draw the general premise that these two modes can be implemented: First, the school has the ability; Second, the enterprise has the benefit; Third, the resources are guaranteed. Of course, G School and M District Education College are typical representatives of promoting education informatization. More schools in S City (usually some schools with better education informatization) adopt the general “purchase-application†model. There is a higher demand for funds. As mentioned above, “the lack of personnel, funds and resources is still the constraint of education development and education informationization in rural poverty-stricken areas for some time to come.†Faced with the situation of fewer people, lack of funds and short resources, poor rural areas must It is conceivable to learn from the success of the successful experience of education informatization in developed regions. IV. Education Information Construction in the "Thirteen Five-Year" Rural Poverty Areas Models and Strategies Faced with many problems in the process of education informatization in rural poverty-stricken areas, only by adopting a more targeted promotion model can we effectively overcome problems and difficulties and better advance the development of education informationization. The author believes that the TPPP model can effectively solve these problems in education poverty alleviation. The so-called TPPP is an English translation abbreviation of the Transfer PublicPrivate Partnership based on transfer payment. The TPPP model requires the active participation of the central or provincial government on the one hand, and uses the scale advantage to attract social enterprises to join relevant businesses and provide relevant The service then sends the business and services to the grassroots level, thereby enabling the partners to achieve more favorable outcomes than expected individual actions. In the field of education informatization, the TPPP model should start from the four aspects of network, terminal, system and resources: in terms of network, the central and provincial governments should stand at the height of precise poverty alleviation and pay full attention to families and individuals in rural poverty-stricken areas. Into the problem, and the relevant agreements with operators to give preferential access to households and students in rural poverty-stricken areas (especially mobile Internet) (or to pay by central and provincial governments), so that poor rural areas can Make more money into the application of information technology; on the other hand, pay special attention to the promotion and application of smart phones and tablets in rural poverty areas. It should be pointed out that with the development of technology, smartphones and tablets are generally on the whole. Seeing that the price is not high, you can follow the model of the previous home appliances to the countryside, and further reduce the price through the government to take a little, the company pastes a little, the masses slap a little, and give preferential treatment to families and students in poor rural areas; in terms of system, actually Schools in rural poverty-stricken areas have a lot of platform construction or a blank paper for system development. Low seeking and high degree of homogenization, the construction of “light application†can effectively meet their needs. The central and provincial governments can cooperate with well-known domestic Internet companies and develop corresponding systems based on their existing infrastructure and platform tools. Then, through cloud deployment, the application of schools and individuals in rural poverty-stricken areas can be realized. With the interaction of home-school and daily management as the core, and then accessing resources and other functions, the small-scale construction and large-scale application of school informationization can be realized. In terms of resources, Encourage and guide domestic well-known video resource enterprises to screen out content suitable for students to watch, and open a “student number†for preferential use by primary and secondary school students. On this basis, the government purchases will give greater benefits to students in rural poverty-stricken areas. In addition, according to the reality of education development and education informationization in rural poverty-stricken areas, the author believes that seven strategies should be adopted to effectively promote education informationization: (1) Cost input: The principle of low cost and high cost performance is faced with the weak situation of people, finances and materials. The education informationization work in rural poverty-stricken areas should be avoided, and the low-cost and cost-effective promotion strategy is adopted. In terms of hardware and software, it is necessary to select a technical solution that requires low network bandwidth requirements, low configuration requirements for informationized terminal equipment, and low maintenance cost in the later stage; in terms of implementation and operation and maintenance, it is necessary to select labor cost as low as possible and low time cost. , the construction path with low operation and maintenance costs. When there are multiple options in the construction of information technology, it is necessary to carefully compare various explicit and implicit costs, and make more choices from the perspective of cost saving. For example, in the choice of cloud services, rural poor areas can replace private clouds with more cost-effective public clouds; in the choice of hardware and terminals, poverty-stricken counties should consider cost-effective, lightweight and practical products. (2) Operation terminal: The mobile terminal is the main and the PC end is the auxiliary. The information terminal equipment is mainly divided into two types: the PC end and the mobile end. Different terminals correspond to different technical paths. In the choice of user terminals, the author believes that education informatization in rural poverty-stricken areas should mainly target the mobile terminal as the target terminal instead of the traditional PC. There are four reasons for this: First, the current rural households can be used for Internet access. Smartphone coverage is much higher than PC coverage. Selecting mobile can solve the problem of Internet access coverage. Secondly, from the perspective of home-school interaction, mobile phones are good for reaching the parents in the first time, in parents and The school has set up a channel for instant communication and interaction. Third, the mobile Internet era has cultivated new habits of the public, giving such a habit to promote education informatization, users will have better acceptance and lower learning costs; With the development of technologies such as HTML5, the current mobile terminal can also realize almost all PC-side functions, and the mobile terminal development cost based on mobile web applications has a significant drop compared with the native application. Of course, the mobile terminal does not mean that the PC end is completely abandoned. The PC side can be used as a good auxiliary for the mobile terminal. For example, the management background with various contents and complicated forms can be placed on the PC side for a small number of teachers and administrators. (III) Promotion strategy: In order to promote the development of education informatization in rural poverty-stricken areas, it is necessary to adhere to the principle of regional integration and promotion. This is divided into two levels. First, the overall planning of regional space, that is, information construction needs to be promoted as a whole, concentrated and synchronously throughout the region. The significance of this is to effectively lower the unit's informatization construction, management and operation and maintenance costs by means of large-scale promotion. Reducing pressure on software and hardware facilities and human resources, responding to the requirements of low-cost information construction in poverty-stricken areas; second, coordinating the construction content, that is, starting from the current situation and actual needs of the region, prioritizing the projects to be built Scientific scheduling, formulate the near, medium and long-term construction plans of urban and rural schools, so that the application of educational information in the region can be promoted in an orderly manner, gradually improved and enriched, and avoid problems such as separate construction, redundant construction, and blind construction. And the drawbacks. (IV) Construction content: provide basic functional protection Different from the comprehensive flowering, fine customization and in-depth exploration of education informatization in economically developed regions, the construction of educational informatization in rural poverty-stricken areas should focus more on the protection of basic functions, namely in teaching and management. At least the basic ability to meet the basic information needs of teachers, students, parents, and managers, and services are often referred to as the "guarantee" function. “Bottom guarantee†does not mean superficialization and simplification of functions, but a high degree of generalization and conciseness of general functions. Such basic functions should be highly flexible and open on the one hand, and can be used in a variety of different demand scenarios; on the other hand, they should have good scalability so that system functions can be further optimized and upgraded in the future. . (5) User experience: easy to use, easy to operate Parents and teachers are the main users of rural poverty education information services. Under the current situation that the information literacy level of parents in rural poverty-stricken areas is unknown and information technology full-time teachers are scarce, it is necessary to make this part of the group happy to try and apply education informationization. Information products must be low in learning cost and easy to operate. Simple operation is reflected in the ease of use of interfaces and functions. It is necessary to convert professional information functions into organizations and descriptions that are easy for the public to understand, so that various functions are clear and intuitive, and at a glance; second, it is reflected in the convenience of business processes. It is necessary to remove unnecessary operation links in the information system as much as possible, improve work efficiency and save time for users; thirdly, it is reflected in the popularization of media channels, and the software tools on which information applications depend should be easy to install and use, without harshness. Equipment configuration requirements, with a good user base. (6) Network security: pay attention to security protection and improve security mechanism At present, the Party Central Committee and the State Council have attached great importance to cybersecurity. While the education informationization work in rural poverty-stricken areas is actively carried out, it must also pay attention to cyber security work and improve its own security protection capabilities. First of all, when selecting educational information products, we should focus on the security factors of data storage, communication transmission, front-end applications, etc., select the system with good security guarantee, and pass the standard security certification products. Secondly, it should be carefully Identify the source of the manufacturer and select the supplier with the information security service qualification as much as possible. Finally, an effective information security management and emergency response mechanism should be developed. Once the product is put into use, once new data security risks and vulnerabilities are discovered, it can be quickly and Steady handling, at the same time do a good job of manager training, strict management of data addition, deletion, query, modification, etc., to avoid data security incidents caused by extensive operation of managers. (VII) Development planning: focusing on long-term and sustainable development The education informatization work in rural poverty-stricken areas can not only take into account the present, but also focus on long-term sustainable development. Some basic work is particularly important. First, we should choose a platform with good universality and extensibility. It can introduce applications from different developers for different scenarios through a unified interface, avoiding the difficulty of integration of other functions due to the closedness of the platform. We should choose a manufacturer with strong strength and strong “moat river†in core technology as a partner, so that education informationization in rural poverty-stricken areas can be promoted smoothly and effectively, avoiding the high conversion cost and technology migration risk caused by switching suppliers. . V. Realizing the "Everyone" through the mature platform is the inevitable choice to promote education informationization in rural poverty-stricken areas After sorting out the patterns and strategies, it is necessary to discuss the core issue of promoting education informatization in rural poverty-stricken areas, that is, how to effectively improve the teaching level of educational informationization. The key to information technology to benefit from education and teaching is to directly play a role in "people". When the "main road" of broadband network, as well as the "goods" of educational applications and teaching resources, the focus of education informationization will be emphasized. On the core issue of how to deliver "goods" from the "main road" to every "person", that is, the problem of "learning space for everyone" in the "three links and two platforms." This is the reason why the "Everyone's Pass" is clearly listed in the "Thirteenth Five-Year Plan for Education Informatization" as the top priority of the "13th Five-Year" education informationization. However, judging from the actual situation of the construction of “everyone pass†at present, there are three general problems in the overall situation. These three problems are particularly prominent in rural poverty-stricken areas. First, the construction cost is high. Large-scale platforms such as “network learning space†have high development costs and higher operation and maintenance costs. In poor areas, when education funds are scarce, it is impossible to develop and operate such platforms on their own. Second, the hardware threshold is high. The current “everyone†is mainly based on computer-side development. In fact, families and schools in poor rural areas generally lack computers that access the Internet. Third, application requirements are high. The current network learning space is complicated in operation, low in user friendliness, and requires high application to operators. Teachers and students often appear to be unwilling, unwilling to use, not in love, and no longer used. The construction of "everyone-to-people" in rural poverty-stricken areas must be judged from the macroscopic level. It is necessary to understand the external development situation, but also to understand the current construction reality, change the construction ideas, lower the application threshold, and introduce the "Internet +" thinking. "Everyone passes." First, we must change from “self-built and self-use†to “use for me†to effectively reduce construction costs. The so-called "used for me" means to fully pay attention to and make good use of the mature systems, technologies and resources in the market, to avoid the "self-built and self-contained" work, and secondly, to change from "desktop" to "mobile". Effectively reduce the hardware threshold; third, to change from "re-application" to "light application", effectively reducing the application threshold. At present, many well-known Internet companies in China have the prototype of “network learning spaceâ€. Most of these products use the mobile terminal as the application platform. The application threshold is low and the user-friendliness is high. It has been widely accepted by the public. It can solve the problem of “last mile†of education informationization, and the huge education group and huge education market have great appeal to these enterprises, which is enough to attract them to invest in the TPPP mode of “network learning spaceâ€. It can be said that the realization of "everyone" through the mature platform is an inevitable choice for promoting education informationization in rural poverty-stricken areas. 6. Education informationization construction plan for rural poverty-stricken areas According to the above-mentioned model and strategy, combined with the current development of education informatization in rural poverty-stricken areas, the author tries to propose an education-informatization promotion plan with application as the core in the next stage of poverty-stricken areas in rural areas. Here are three key points: The most basic "communication" problem is to connect people and people, and to bring together stakeholders in the education field, including students, parents, teachers, school administrators and education administration departments. This can be achieved by building a management and service application based on the mobile social platform. Second, it is necessary to solve the problem of “teachingâ€. It can realize the informationization through the construction of teaching and research platform, integrated teaching evaluation, teacher training, teaching and research resource sharing and other functions. Teacher's teaching support. The third is to solve the problem of "learning". Through the construction of a teaching platform, integration of student homework guidance, pre-course guidance, classroom teaching and other functions, to achieve information support for students' learning support; as the underlying data source of three platforms, rural The “educational data center†in poverty-stricken areas can be deployed in a hybrid cloud. The platform provides users with unified identity authentication and unified portals in both PC and mobile forms. The overall plan is shown below. (1) Management service platform The platform is targeted at parents, teachers, students, school administrators, and the education administration. The basic functions of the platform mainly include three aspects. First, the interaction between home and school, this function is mainly for teachers and parents, so that the two sides can conduct dialogues and exchanges in a timely manner, and enhance the participation of parents in school education. This function can also enable parents who work outside the home to achieve good and classroom teachers. Communication, solve the problem of left-behind children's home-school communication; Second, office management, this function is mainly for teachers and school administrators, providing information functions such as attendance, approval, leave, etc., to save paper, manpower and other office costs, improve daily administration The efficiency of transaction processing; the third is school management. This function is mainly for school administrators and education administration departments. It manages the core data of teachers, students and parents, and depicts and outlines the overall operational status of educational institutions. In addition to the above three functions, the poverty-stricken county can also independently determine the functions of other management service platforms according to their actual conditions. In the technical path, mobile social software can be selected as the carrier of the platform, and the personnel, organization and system are connected through the mobile web application to realize identity-based application provisioning and service push [8]. In order to save costs, the data and applications in the management service platform can be deployed on a public cloud with sufficient security for users to access and use. Some key personnel and institutional data can be deployed in a private cloud at the county level, either mirrored or exclusively, to allow managers to better analyze and manage data. (2) Teaching platform The platform is targeted at students, teachers, and school administrators. Its functions mainly include three aspects. The first is the course guidance, that is, the teacher creates and organizes the teaching content, and provides it to the students in the form of online courses for students to prepare before class and review after class, so that students can arrange the progress more flexibly and autonomously. Second, classroom teaching, ie Through the introduction of information tools in the classroom teaching process, students' understanding of knowledge is enhanced, and the data collection of students' learning process is realized. Thirdly, homework counseling, that is, through online system, enables students to practice tasks after completing the teacher's arrangement. At the same time, it is possible to directly view information such as task knowledge points, problem solving ideas, and answering processes, and provide learning support for students to practice after class and consolidate their knowledge. In addition to the above three functions, the poverty-stricken counties can also independently determine the functions of other teaching platforms according to their actual conditions. In terms of technology, the course guidance module in the teaching platform can adopt the micro-course video recording mode, and the teacher records the teaching content through simple equipment such as a camera, a microphone, and the like, and a simple technical means such as a PPT recording screen. The classroom teaching module can take the form of combining the flat-panel TV and projector of the classroom with the online teaching platform, so that the teacher can present the students with rich and colorful learning resources in the teaching process. The qualified school can also explore the use of the tablet in the classroom. A new model for teaching activities in computers. The homework tutoring module can adopt a simple, low-cost electronic pen, tablet, drawing tool and other recording schemes. The teacher records the problem-solving process as a video by handwriting and recording for students to play and browse. In addition, the student's learning data can be automatically organized to form a knowledge set such as wrong questions and problems, providing students with personalized learning support. (3) Teaching and research platform In addition to teachers, the target group of the platform includes school administrators and educational administration departments related to teaching research and teaching evaluation. The platform mainly covers three types of functions. The first is the sharing of teaching and research resources. With the online video library, knowledge base, courseware library, test database, database, etc., the materials and experience of education and teaching are shared among teachers, teaching and research groups, schools and other levels. Second, teaching Evaluation, through the comprehensive recording of teachers' performance in the classroom, using a combination of automation and human assessment, quantitative evaluation of teachers' teaching effects, helping teachers optimize and improve the teaching process; third, teacher training, combined with teaching The evaluation results provide teachers with personalized learning objectives, and open up a learning and communication space for teachers through online and offline integration to promote teachers' professional learning and development. In terms of technology, the teaching and research resource sharing module can be implemented by deploying a private cloud disk in the county. Under the condition of sufficient network bandwidth, a public cloud disk mode with higher cost performance can also be adopted. The teacher training module and the teaching evaluation module can be realized by deploying the cloud recording and broadcasting system in the classroom, developing and deploying the classroom teaching evaluation system and the teacher training system. Conclusion The promotion of education informatization in rural poverty-stricken areas is related to the overall development of education in poverty-stricken areas. It is also related to the success or failure of the central government's fight against poverty. As the chairman comrades pointed out, "It is an important task for poverty alleviation and development to let children in poverty-stricken areas receive good education. It is also an important way to block the intergenerational transmission of poverty." Promoting education informatization in rural poverty-stricken areas is a long-term and difficult process. Finding the right mode and finding the right strategy. The development of education informatization in rural poverty-stricken areas will also enter the fast lane, and the “curve overtaking†of education development will follow. Come. Stainless Steel Frypan With Lid Stainless Steel Non Stick Pan,Stainless Steel Frypan With Lid,Stainless Steel Skillet With Lid,Stainless Steel Frying Pan With Lid SUZHOU JIAYI KITCHENWARE TECHNOLOGY CO.,LTD , https://www.jiayikitchenware.com